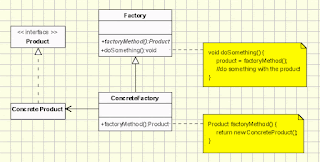
Abstract
factory design pattern
It is a factory of
factories. Abstract factory returns a list of factories that produces related
items.
E.g.: A car
assembler company can assemble a Ford car and a BWM car.
Based on a client
can ask to get a Ford or a BMW. So if there is 1 single factory, that factory
has to implement all the various items it can generate for all different brands.
Additionally the assembler has to keep track of the brand. Otherwise he may
order a Ford “car body” and a BMW “interiors”. This will result in
incompatibility of the parts. Hence it makes sense to have sub-factories. The
assembler then will get back a factory instance, and can use it to get all
compatible parts of a car.
public class AbstractFactory {
private static final AbstractFactory instance = new AbstractFactory();
private AbstractFactory()
{
super();
}
public static AbstractFactory
getInstance() {
return instance;
}
public I_Factory
getFactory(String brand) {
if(brand.equals("ford")) {
return Ford_Factory.getInstance();
}
else {
return BMW_Factory.getInstance();
}
}
}
public interface I_Factory {
public I_CarPart
getPart(String partName);
}
public class BMW_Factory implements I_Factory {
private static final I_Factory instance = new BMW_Factory();
private BMW_Factory() {
super();
}
public static I_Factory
getInstance() {
return instance;
}
@Override
public I_CarPart
getPart(String partName) {
if(partName.equals("body")) {
return new BMW_Body();
}
else {
return new BMW_Interiors();
}
}
}
public class Ford_Factory implements I_Factory {
private static final I_Factory instance = new Ford_Factory();
private Ford_Factory() {
super();
}
public static I_Factory
getInstance() {
return instance;
}
@Override
public I_CarPart
getPart(String partName) {
if(partName.equals("body")) {
return new Ford_Body();
}
else {
return new Ford_Interiors();
}
}
}
public interface I_CarPart {
public void description();
}
public class Ford_Body implements I_CarPart {
@Override
public void description() {
System.out.println("Ford body");
}
}
public class Ford_Interiors implements I_CarPart {
@Override
public void description() {
System.out.println("Ford interiors");
}
}
public class BMW_Body implements I_CarPart {
@Override
public void description() {
System.out.println("BMW body");
}
}
public class BMW_Interiors implements I_CarPart {
@Override
public void description() {
System.out.println("BMW interiors");
}
}
public class MainClass {
public static void main(String[]
args) {
System.out.println("Assembling ford car");
I_Factory
factory = AbstractFactory.getInstance().getFactory("ford");
factory.getPart("body").description();
factory.getPart("interiors").description();
System.out.println("Assembling BMW car");
factory
= AbstractFactory.getInstance().getFactory("BMW");
factory.getPart("body").description();
factory.getPart("interiors").description();
}
}
Result:
Assembling ford car
Ford body
Ford interiors
Assembling BMW car
BMW body
BMW interiors
Code link : https://github.com/sksumit1/DesignPatterns
Code link : https://github.com/sksumit1/DesignPatterns